Kubernetes dashboard is a web-based user interface which provides information on the state of the Kubernetes cluster resources and any errors that may occur. The dashboard can be used to deploy containerized applications to the cluster, troubleshoot deployed applications, as well as the general management of the cluster resources.
The deployment of Deployments, StatefulSets, DaemonSets, Jobs, Services and Ingress can be done from the dashboard or from the terminal with kubectl. if you want to scale a Deployment, initiate a rolling update, restart a pod, create a persistent volume and persistent volume claim, you can do all from the Kubernetes dashboard.
Source : kubernetes.io
Install kubectl on Linux
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/`curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt`/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
chmod +x ./kubectl
sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectlConfirm your installation of kubectl.
$ kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"22", GitVersion:"v1.22.2", GitCommit:"8b5a19147530eaac9476b0ab82980b4088bbc1b2", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-09-15T21:38:50Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.8", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"22", GitVersion:"v1.22.2", GitCommit:"8b5a19147530eaac9476b0ab82980b4088bbc1b2", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-09-15T21:32:41Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.8", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}Configure Kubectl
The kubectl tool looks for a file named config in the $HOME/.kube directory, but a separate file can be specified using --kubeconfig option. The kubeconfig files helps you to organize information about clusters, users, namespaces, and authentication mechanisms.
$ ls $HOME/.kube/config
/home/root/.kube/configcat .kube/config
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUJWakNCL3FBREFnRUNBZ0VBTUFvR0NDcUdTTTQ5QkFNQ01DTXhJVEFmQmdOVkJBTU1HR3N6Y3kxelpYSjIKWlhJdFkyRkFNVFUzTkRNNE16ZzJOVEFlRncweE9URXhNakl3TURVeE1EVmFGdzB5T1RFeE1Ua3dNRFV4TURWYQpNQ014SVRBZkJnTlZCQU1NR0dzemN5MXpaWEoyWlhJdFkyRkFNVFUzTkRNNE16ZzJOVEJaTUJNR0J5cUdTTTQ5CkFnRUdDQ3FHU000OUF3RUhBMElBQkpsb3NSY1FRTHlsL28yeFltQ0l4eHdsZ1F3ZTdlU1dxQmNaRFQ3Q2xJcXoKNnB4R24yb2w3MHM3N3dpcTNaRnkrSW0vdFhHSW16Y3N6MHFNYUpjUy9rV2pJekFoTUE0R0ExVWREd0VCL3dRRQpBd0lDcERBUEJnTlZIUk1CQWY4RUJUQURBUUgvTUFvR0NDcUdTTTQ5QkFNQ0EwY0FNRVFDSUVJcjZ6NGRMUUw1Ck8wSUN3ejBWUEdhYUs0bEU3bFU3SmJXTWhoRk9vcDh1QWlBKzZhcG9NMFVtZ1IxYkFBeWNaS0VHL3AzQWRhWmEKMWV3TGxmUkxiWkJwa3c9PQotLS0tLUVORCBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCg==
server: https://127.0.0.1:6443 #CHANGE TO LB OR MASTER NODES
name: default
contexts:
- context:
cluster: default
user: default
name: default
current-context: default
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: default
user:
password: 76dd75552cb14f3085445277a2091c6c
username: adminGet the Cluster URL, CA data, and user credentials then substitute in the file.
Deploy Kubernetes Dashboard
The default Dashboard deployment contains a minimal set of RBAC privileges needed to run. You can deploy Kubernetes dashboard with the command below.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/master/aio/deploy/recommended.yamlYou can as well download and apply the file locally:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/master/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
kubectl apply -f recommended.yamlSet Service to use NodePort
This will use the default values for the deployment. The services are available on ClusterIPs only as can be seen from the output below:
$ kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.104.220.36 <none> 8000/TCP 23s
kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.108.11.22 <none> 443/TCP 25sPatch the service to have it listen on NodePort:
kubectl --namespace kubernetes-dashboard patch svc kubernetes-dashboard -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'Confirm the new setting:
$ kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard -o yaml
...
spec:
clusterIP: 10.108.11.22
clusterIPs:
- 10.108.11.22
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ipFamilies:
- IPv4
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
ports:
- nodePort: 30506
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8443
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
status:
loadBalancer: {}- NodePort exposes the Service on each Node’s IP at a static port (the NodePort). A ClusterIP Service, to which the NodePort Service routes, is automatically created.
$ vim nodeport_dashboard_patch.yaml
spec:
ports:
- nodePort: 32000
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8443
EOFApply the patch
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard patch svc kubernetes-dashboard --patch "$(cat nodeport_dashboard_patch.yaml)"Check deployment status:
$ kubectl get deployments -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper 1/1 1 1 86s
kubernetes-dashboard 1/1 1 1 86sTwo pods should be created – One for dashboard and another for metrics.
$ kubectl get pods -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper-7b64584c5c-xvtqp 1/1 Running 0 2m4s
kubernetes-dashboard-566f567dc7-w59rn 1/1 Running 0 confirm if the service was actually created.
$ kubectl get service -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.103.159.77 <none> 8000/TCP 8m40s
kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.101.194.22 <none> 443:32000/TCP 8m40Create Admin service account
start by creating a Service Account manifest file. I’ll name the service account admin.
$ vim admin-sa.yml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin
namespace: kube-systemadmin is the name of the service account to be created.
Create a Cluster Role Binding
Next is to assign the service account created a cluster role binding of cluster-admin.
$ vim admin-rbac.yml
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin
namespace: kube-systemReplace admin with the name of the service account you created in step 1.
Apply the file.
kubectl apply -f admin-rbac.ymlObtain admin user token
print the generated token for a service account by using the kubectl command.
Set a variable to store the name of the service account.
SA_NAME="admin"Then run the command below to print the token for the admin user created.
kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep ${SA_NAME} | awk '{print $1}')Output:
Name: admin-token-mm9jd
Namespace: kube-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: admin
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: 80fade4b-4270-11ea-9fe4-005056ba45bd
Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
Data
====
token: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI9IiJ9.eyJpc7MiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Iiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9uYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJrdWJlLXN5c3RlbSIsImt1YmVybmV0ZXMuaW8vc2VydmljZWFjY291bnQvc2VjcmV0Lm5hbWUxOiJqa211dGFpLWFkbWluLXRva2VuLW1tOWpkIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pby9zZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC9zZXJ2aWNlLWFjY291bnQubmFtZSI6ImprbXV0YWktYWRtaW4iLCJrdWJlcm5ldGVzLmlvL3NlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50L3NlcnZpY2UtYWNjb3VudC51aWQiOiI4MGZhZGU0Yi00MjcwLTExZWEtOWZlNC0wMDUwNTZiYTQ1YmQiLCJzdWIiOiJzeXN0ZW06c2VydmljZWFjY291bnQ6a3ViZS1zeXN0ZW06amttdXRhaS1hZG1pbiJ9.uMC2ydeHF4jVA5tnKFbBeHRvc4NWqL920jigk2FDeduUdBuFhsNyDcscmL-pBbWHG5KKwOAEuAAeyNaknaHsDadNnbLpp4AMZTTdr22FEp-_v7MfIEQm3QWmq-c0ykpdrzUzGmk5Q3JIpfqeorDI0lZd52-DF4IVMw3VtTNp6ZMHdieQUNRnCEyfs98raCTRAotiXZQaMvmRW5s9peu5hfxM71jufg-Qzmflr9nO-dY2dOHh1WZcKhJqfNfB73GYX2TQlUlurV4Oy0-2CpUUpJ1HAjcSHzKGuSrMUAMAhRwhbZZXhwvbQ6Ei_9Vv2PkD8_Pw9c-k9x-bblFSAqyFhA
ca.crt: 1025 bytes
namespace: 11 bytesCopy the contents in token key.
Accessing Kubernetes Dashboard
Service deployment was assigned a port 32000/TCP.
# Example
https://103.89.1.230
:32000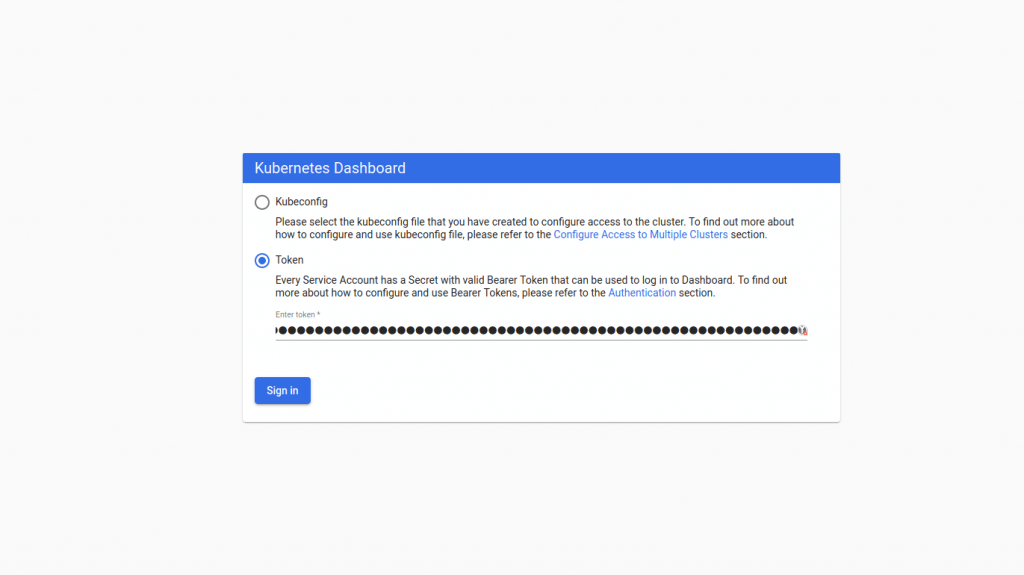
Nginx Ingress:
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: k8s-dashboard
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/secure-backends: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: "true"
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- k8sdash.mydomain.com
secretName: tls-secret
rules:
- host: k8sdash.mydomain.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: kubernetes-dashboard
servicePort: 443